Batteries play a crucial role in powering various electronic devices, vehicles, and equipment. Lead-acid batteries and lithium-ion batteries are two popular types of batteries. In this article, we will discuss the differences between these two battery types in terms of their construction, working principles, efficiency, lifespan, cost, and common applications.
What Is Lead Acid Battery

source:unplash.com
Lead-acid batteries are a type of rechargeable battery that uses lead electrodes and sulfuric acid electrolytes that are commonly used in cars, boats, and uninterruptible power supplies (UPS) due to their reliability and low cost. The lead-acid battery is the oldest type of rechargeable battery, having been invented in 1859 by Gaston Planté.
How Does Lead Acid Battery Work?

source:unplash.com
A lead-acid battery works by converting chemical energy into electrical energy. It consists of a series of lead plates (electrodes) immersed in an electrolyte solution of sulfuric acid and water. The plates are made of a porous material coated with a lead oxide paste. When the battery is connected to a load, a chemical reaction occurs between the lead plates and the sulfuric acid electrolyte. This reaction creates an electrical current that flows through the load, such as a car engine starter or a lighting system.
The lead-acid battery has two types of electrodes: the positive electrode (also called the anode) and the negative electrode (also called the cathode). The negative electrode is made of lead, while the positive electrode is made of lead dioxide.
When the battery is charged, electrical energy is used to convert the lead oxide paste on the electrodes back into lead and lead dioxide. This process is called charging. During discharging, the lead and lead dioxide react with the sulfuric acid to create lead sulfate on both plates, releasing electrical energy in the process.
What Is lithium-Ion Battery

source:unplash.com
Lithium-ion batteries are rechargeable batteries that use lithium ions as the main charge carrier. These batteries are commonly used in portable electronic devices, electric vehicles, and power tools due to their high energy density and lightweight. The first lithium-ion battery was invented in 1985 by John Goodenough, Stanley Whittingham, and Akira Yoshino.
How Does Lithium-Ionn Battery Work

source:unplash.com
Lithium-ion batteries are rechargeable batteries commonly used in portable electronic devices, electric vehicles, and energy storage systems. They work by using lithium ions to transfer energy between two electrodes: a positive cathode and a negative anode.
During charging, lithium ions are extracted from the cathode and move through an electrolyte to the anode, where they are stored. The process is reversed during discharge, with the lithium ions moving from the anode back to the cathode, releasing energy in the process.
The cathode typically contains lithium cobalt oxide, lithium manganese oxide, or lithium iron phosphate, while the anode is usually made of graphite. The electrolyte is a liquid or gel containing lithium salts that allow for the flow of ions between the electrodes.
Lead Acid Battery vs. Lithium Ion Battery

source:unplash.com
These two batteries have their own advantages and disadvantages in many aspects. Let’s make a comparison.
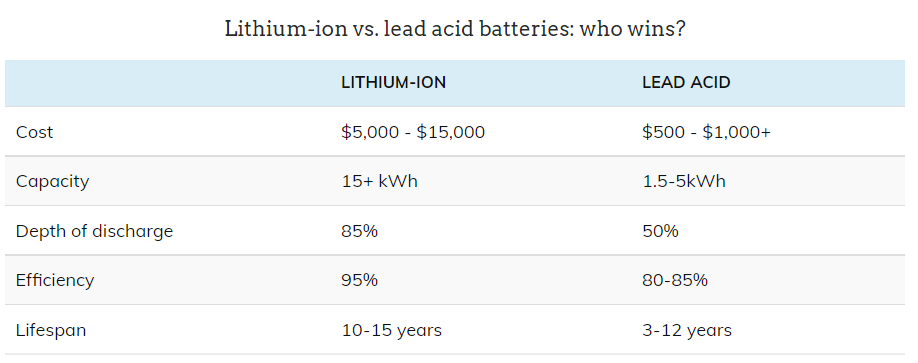
source:https://news.energysage.com/lithium-ion-vs-lead-acid-batteries/
Cost

source:unplash.com
While lithium-ion batteries generally have a higher upfront cost compared to lead-acid batteries, they offer several advantages that can offset the initial expense. For instance, lithium-ion batteries have a longer lifespan and higher energy density than lead-acid batteries, making them more space-efficient and cost-effective in the long term. Additionally, lithium-ion batteries require minimal maintenance and can be left unused for long periods without deteriorating, whereas lead-acid batteries need regular maintenance, such as checking and topping up electrolyte levels and equalizing cells to prevent sulfation. Therefore, while lead-acid batteries may be cheaper upfront, lithium-ion batteries may offer a better overall value proposition, depending on the specific application and requirements.
Life Span

source:unplash.com
Lithium-ion batteries generally have a longer lifespan than lead-acid batteries. The average lifespan of a lithium-ion battery is around 10 to 15 years, depending on the usage and charging patterns, while the average lifespan of a lead-acid battery is around 3 to 12 years.
One of the factors that contribute to the longer lifespan of lithium-ion batteries is their chemistry. Lithium-ion batteries use a different chemistry than lead-acid batteries, which allows them to hold a charge for a longer period of time without losing capacity. In addition, lithium-ion batteries are not as prone to sulfation, which is a common problem with lead-acid batteries that can reduce their lifespan.
Another factor that contributes to the longer lifespan of lithium-ion batteries is their ability to withstand deep cycling. Deep cycling refers to the process of fully discharging and then recharging a battery. While lead-acid batteries can be damaged by deep cycling, lithium-ion batteries are designed to handle it without significant degradation in performance.
Overall, the longer lifespan of lithium-ion batteries makes them a more cost-effective option in the long run, despite their higher initial cost. However, it’s worth noting that the lifespan of a battery can be affected by a variety of factors, including usage patterns, operating temperatures, and charging methods. Therefore, proper maintenance and care are important to ensure that a battery reaches its full potential lifespan.
Efficiency

source:unplash.com
The efficiency of lead-acid batteries is typically around 85%, while the efficiency of lithium-ion batteries is around 90-95%. Despite this, lithium-ion batteries are generally more efficient than lead-acid batteries, both in terms of energy efficiency and charging efficiency.
1. Energy Efficiency
Lithium-ion batteries have a higher energy density than lead-acid batteries, which means they can store more energy per unit of weight or volume. This makes them more space-efficient and allows them to power devices for longer periods of time without requiring a recharge. In addition, lithium-ion batteries can discharge more of their stored energy before their voltage drops, which means they can provide more usable energy to power a device.
2. Charging Efficiency
Lithium-ion batteries are also more efficient when it comes to charging. They can be charged at a faster rate and with higher charging currents than lead-acid batteries, which can reduce charging times and increase the overall efficiency of the charging process. In addition, lithium-ion batteries can be charged to a higher capacity without causing damage, which means they can provide more energy per charge cycle than lead-acid batteries.
Common Applications

source:unplash.com
Here are some common applications of lead-acid batteries and lithium-ion batteries in various fields.
1. Lead Acid Battery Applications
- Automobiles: Lead-acid batteries are widely used in automobiles as they are reliable and cost-effective. They are also efficient and can provide large currents for short periods of time, making them ideal for starting an engine. Lead-acid batteries are also relatively maintenance-free and are able to tolerate harsh operating conditions. Additionally, lead-acid batteries are widely recyclable and are not hazardous to the environment. Lead-acid batteries have low internal resistance and can provide high power over long periods of time, making them well-suited for automotive applications.
- Uninterruptible power supplies (UPS): Lead-acid batteries are also used in UPS systems to provide backup power in case of power outages. These systems are commonly used in data centres, hospitals, and other critical facilities. In addition to data centres and hospitals, UPS systems with lead-acid batteries are also widely used in industrial settings to ensure uninterrupted power supply for critical equipment and processes. These batteries are preferred for their ability to handle high discharge currents and their resilience to overcharging. However, the adoption of lithium-ion batteries in UPS systems is increasing due to their higher energy density and longer lifespan, making them a viable alternative for applications that require high performance and reliability.
- Marine vessels: Lead-acid batteries have a wide range of applications in the marine industry, from powering electrical systems on boats and yachts to providing starting power for engines. In combination with other power sources, such as generators or solar panels, they can be used to power navigation lights, radios, radar systems, and other electronic equipment on board. Smaller vessels, like electric trolling motors or outboard engines, can also be powered by lead-acid batteries. A key advantage of using lead-acid batteries in marine applications is their ability to withstand harsh marine conditions. Their robust and corrosion-resistant casing protects them from exposure to saltwater and other corrosive substances. In addition, they are designed to operate effectively at a wide range of temperatures, making them an ideal choice for marine environments where temperature variations can be significant.
- Golf carts and other small electric vehicles: Lead-acid batteries are commonly used in golf carts and other small electric vehicles.
- Security systems: Lead Acid batteries are commonly used in security systems due to their low cost and straightforward charge/discharge cycle. These batteries can provide reliable, long-lasting power to security systems, allowing them to remain operational during power outages and other disturbances. Lead Acid batteries are also known to be able to provide a higher power output than other battery types, making them ideal for powering motors, pumps, and other security components.
2. Lithium Ion Battery Applications
- Consumer electronics: Lithium-ion batteries are commonly used in smartphones, laptops, and tablets. They have a high energy density, which means they can store a lot of energy in a small space. Additionally, lithium-ion batteries typically have lower self-discharge rates, meaning they will retain charge for a longer period of time than other types of batteries. They also have no memory effect, meaning they can be recharged before being completely discharged, without loss of performance which is very much in line with the application scenario for consumer electronics.
- Electric vehicles: Lithium-ion batteries are used to power electric vehicles, including cars, buses, and bikes. They have a high power density, which means they can deliver a lot of power quickly.
- Renewable energy systems: Lithium-ion batteries are used to store energy in renewable energy systems, such as solar and wind power. They are often used in combination with other types of batteries to provide reliable and efficient energy storage.
- Aerospace and aviation: Lithium-ion batteries are used in aerospace and aviation applications, such as satellites and unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs). They are becoming the preferred choice due to their high energy density and light weight. This significantly reduces the amount of payload required for long-range aircraft, which in turn increases payload capacity and range. Lithium-ion batteries also have a higher power-to-weight ratio compared to other types of batteries, allowing for more efficient and powerful engines and other aviation components.
- Medical devices: Lithium-ion batteries are used in medical devices, such as portable oxygen concentrators and insulin pumps. They are used because they are small and lightweight, and can provide reliable power for long periods of time.
Conclusion
In conclusion, it’s important to consider factors such as the environment, temperature, and maintenance requirements when choosing a battery. For example, lead-acid batteries are better suited for stationary applications and cold temperatures, while lithium-ion batteries perform better in mobile applications and hot temperatures. Overall, understanding the strengths and weaknesses of both types of batteries is crucial in making an informed decision for your specific needs.






